Skin Cancer Screenings and Total Body Skin Exams
Dermatologists are specially trained to recognize and differentiate between benign moles, freckles, and other skin lesions from potentially harmful or cancerous ones. Early identification of suspicious lesions can prompt further evaluation or biopsy if necessary, significantly improving the chances of successful treatment and outcomes.
At SeaCoast Skin Surgery, we prioritize your skin health with comprehensive skin cancer screenings. Our expert dermatologists utilize their extensive training and experience to conduct detailed examinations, ensuring that any signs of skin cancer are detected early. Regular screenings are essential for everyone, especially those with a history of sun exposure, tanning bed use, or a family history of skin cancer.
Don't wait to take charge of your skin health. Schedule a total body skin exam (TBSE) with our trusted dermatologists at the SeaCoast Skin Surgery today. Early detection is key to effective treatment and maintaining healthy skin. Let us provide you with the peace of mind that comes with thorough and professional skin cancer screening.
Examples of Skin Cancer Screenings
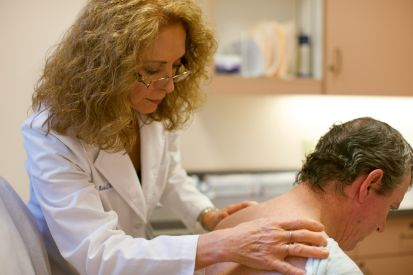
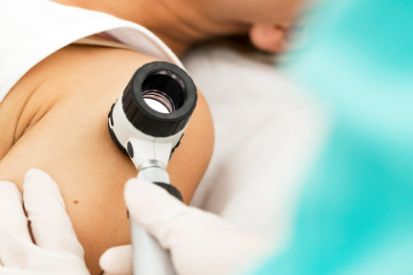
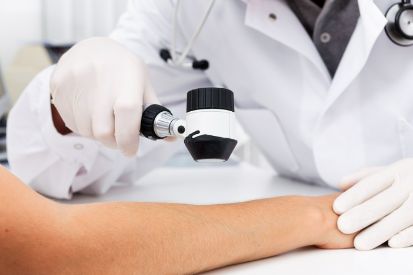
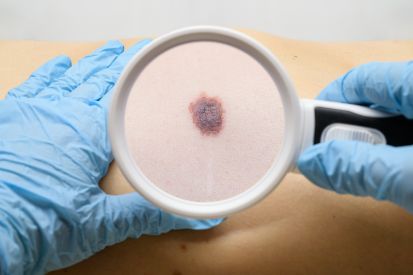
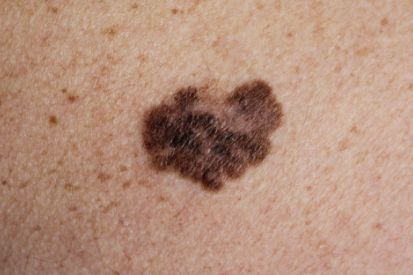

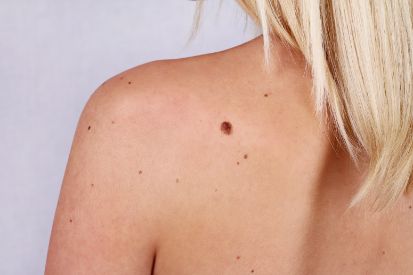
Why Skin Cancer Screenings Matter
When there is an absence of noticeable symptoms and similarities to other—often mild—skin conditions, skin cancer can be stealthy. Your awareness is further limited by areas of your body you rarely—if ever—see yourself.
Getting a full body skin exam by a skin cancer expert at Pinnacle Dermatology ensures that signs of skin cancer do not continue to go unnoticed.
Importance of Early Detection
Once cancer develops, it can grow and spread rapidly. A good example is to think of a house flood. The more that water is allowed to spread out and rise, the greater the damage and the more extensive the clean up will be. In other words, to control the spread of cancer cells, it must be detected early before it has the chance to grow and spread.
Skin cancer can also metastasize into other parts of the body causing you to need treatment not just on the skin, but for other organs as well. This can lead to multiple treatments from more than one specialist.
In short, keeping up with your screening schedules for early detection of skin cancer can save you time, stress, money and more importantly, your life.
Skin Cancer Types That TBSE Helps Detect
There are four main types of cancer that can form on the epidermis, each having different characteristics and risks. A TBSE, or full body skin exam will check for the most common forms of skin cancer:
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): The most common type of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma starts in the basal cells that replenish with new skin cells when the old cells die.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): The second most common type of skin cancer, squamous cell carcinoma begins in the squamous cells that live in the middle and outer skin layers.
- Melanoma: A dangerous form of skin cancer, melanoma develops in the melanocytes that give skin its pigment. Early detection of melanoma is critical for managing this serious form of skin cancer.
- Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC): A rare, yet aggressive type of cancer, Merkel cell carcinoma forms on the outer layer of the skin (once believed to originate from the Merkel cells) and metastasizes to other parts of the body including organs, and tends to recur after treatment.
FAQs: Total Body Skin Exam (TBSE)
The frequency of TBSEs varies based on individual risk factors, personal history, and family history of skin cancer. Generally, it's recommended to have a baseline examination and discuss follow-up intervals with your dermatologist.
No, a TBSE is a non-invasive and painless examination. It involves a visual inspection without any invasive procedures like biopsies unless a suspicious lesion is identified and requires further evaluation.
After the examination, your dermatologist may discuss their findings with you. If suspicious lesions are identified, they might recommend further evaluation through a biopsy or additional tests.
Yes, regular self-examinations of your skin are encouraged. Your dermatologist can teach you how to perform self-checks between professional examinations. Look for changes in moles, new growths, or any irregularities in your skin.
Anyone with a history of skin cancer, multiple moles, or a family history of skin cancer should consider regular TBSEs. Individuals with fair skin, extensive sun exposure history, or a weakened immune system may also benefit.
Sun protection is essential. Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses, and seek shade during peak sun hours to minimize sun damage and reduce the risk of skin cancer.
From our QualDerm Family of Brands: Total Body Skin Exams
What to Expect During Your Total Body Skin Exams
If you are feeling apprehensive about a TBSE for a loved one or yourself, you are not alone. The combination of being disrobed for a full-body inspection and physical contact can make some patients feel more vulnerable than they would during other types of medical exams.
Taking the time to read up on all that is involved in your first full body skin exam and what to expect is a smart step toward managing the experience.
What a Dermatologist Is Looking For During a Full Body Exam
The goal of a TBSE is to check the entire skin—the body’s largest organ—for any signs of skin cancer. This coverage includes the scalp, face, neck, ears, arms, legs, feet, toes, and torso. Special attention will be given to any skin lesions, moles, freckles, and birthmarks.
The dermatologist skin check will document the size, shape, color, and borders of each skin mark. Because detecting changes over time is key to identifying potential skin cancer, annual TBSEs allow for a detailed record to compare from year to year.
If anything appears suspicious, your dermatologist may recommend monitoring the area, scheduling follow-up visits, or performing additional testing. Your dermatologist will discuss any findings with you, as well as explain next steps.
Is a Full Body Skin Exam Painful Or Embarrassing?
At Pinnacle Dermatology, we understand that some patients can feel apprehensive or vulnerable, especially if it’s their first time to receive a full body skin exam. TBSEs are a gentle visual inspection of the body with no physical pain to be expected from the exam itself. However, if you have issues such as chronic pain or tender spots, please let us know so that we can better accommodate you.
Our providers at Pinnacle Dermatology are professionally trained and knowledgeable. We encourage you to share your personal preferences, such as receiving a total full body skin exam from a female dermatologist. Our care team aims to make your experience as comfortable as possible, so please voice any questions, concerns or feelings of apprehension with our care team.
How to Prepare for a TBSE
With the skin being the body’s largest organ, it is important to allow sufficient time for your first and future TBSEs. In addition to timely arrival and expecting to stay the full duration, here are other tips on how to prepare for a full body skin exam, particularly when it is your first time:
- Wash your entire body.
- Wear clothing that is easy to remove.
- Wear shoes that are easy to slip off, and consider wearing shoes without socks.
- Consider skipping the application of makeup.
- Have your complete medical history ready, asking your blood relatives about any family history of cancer.
- Make a list of questions and concerns to discuss with the dermatologist.
- Share notes or photos of any concerning skin marks or changes that you have noticed.
What Happens After the Exam?
While the team at Pinnacle Dermatology always hopes to give patients the “all clear,” there are occasions when something suspicious is found. If so, you can expect our dermatology provider to clearly communicate next steps which may include self-monitoring, follow-up appointments, testing, and potential future treatments.
That aside, after your TBSE you can expect to resume normal activities and plan to come back for a dermatologist skin check next year.
The Importance of Skin Cancer Prevention
When it comes to skin cancer prevention, managing your skin’s exposure to sunlight is first and foremost. The best way to protect your skin from damaging sun exposure is to:
- Make a habit of regular sunscreen use: Choose dermatologist recommended sun protection products such as broad spectrum sunblock of 30 SPF. Apply whenever you’re outdoors, even during cloudy or winter days. Those whose professions or lifestyle involve extended daytime exposure should reapply sunscreen every two hours, or after swimming or profuse sweating.
- Protective clothing and accessories: Skin coverage with clothing and hats are a big help when it comes to sun protection. Wide brimmed hats, UV-blocking sunglasses, full coverage tops and pants, and even rash guards work well to manage exposure.
- Take shelter: Remaining indoors or in the shade—especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the UV rays are strongest—is very effective for skin protection.
Of course, the other core component of skin cancer prevention is to keep up with your skin cancer screening schedule and monitor for changes to the skin as directed by your dermatology provider.
Featured Products for Sun Protection

EltaMD UV Pure SPF 47
For those who want chemical-free active ingredients, EltaMD UV Pure is the ideal daily sunscreen. Great for children and adults, the gentle formula glides on wet or dry skin and rubs in quickly. UV Pure is formulated with purely physical active ingredients which are photostable. 4 oz / 114 g

EltaMD UV Sheer Broad-Spectrum SPF 50
UV Sheer has a lightweight, hydrating formula that feels silky to the touch and light and airy on the skin. It goes on smooth absorbing quickly into skin and helps even out skin tone. This facial sunscreen offers up to 80 minutes of sweat and water-resistance making it the ideal choice for an active lifestyle, hot and humid weather and for anyone looking for a lightweight and hydrating sunscreen to live freely under the sun. UV Sheer is formulated to be compatible on all skin tones without leaving a white cast. 3.0 oz
