Melanoma
Melanoma, the third most prevalent skin cancer in the United States, sees about 50,000 new cases annually. This malignancy originates from melanocytes, the pigment cells determining our skin color and situated in the outermost skin layer, the epidermis. While melanoma typically arises in sun-damaged skin, it has the potential to develop anywhere on the body.
Renowned for their expertise in skin cancer treatment, the professionals at SeaCoast Skin Surgery play a pivotal role in addressing melanoma. Their exceptional training significantly contributes to early detection and effective management. Although melanoma often remains confined to the skin initially, it can progress and spread through lymph or blood vessels, occasionally metastasizing to nearby lymph nodes, distant tissues, or organs. Timely intervention is crucial, underscoring the importance of the specialized skills offered by SeaCoast Skin Surgery in improving outcomes, preventing metastasis, and enhancing overall prognosis.
Despite being less common than other skin cancers, melanoma stands as the deadliest, responsible for approximately 75% of all skin cancer deaths. Annually, the U.S. witnesses around 160,000 new melanoma cases. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light significantly contributes to the risk of developing melanoma. The awareness of this risk factor emphasizes the importance of sun protection measures and regular skin checks for early detection and effective management of melanoma.
Examples of Melanoma
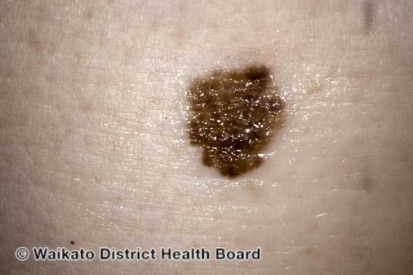
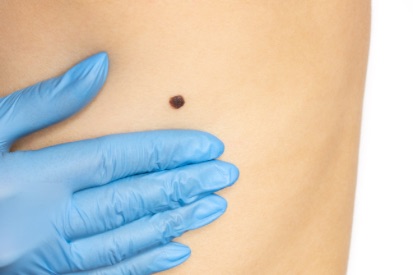
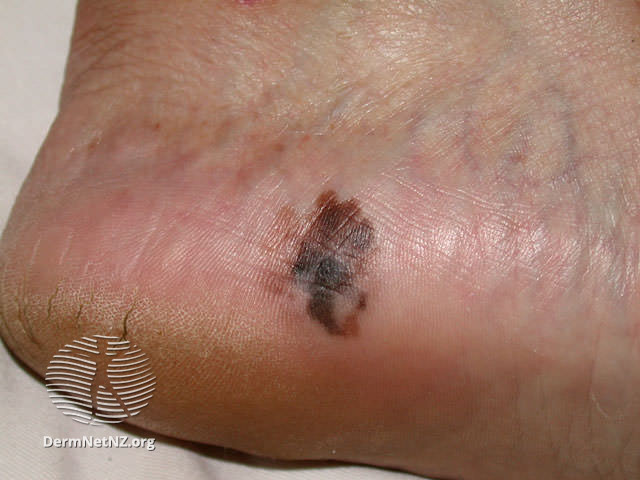
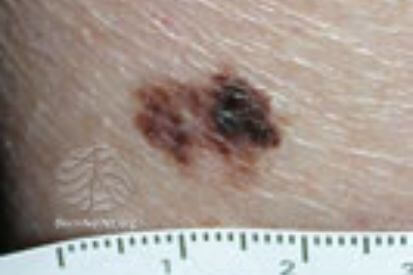
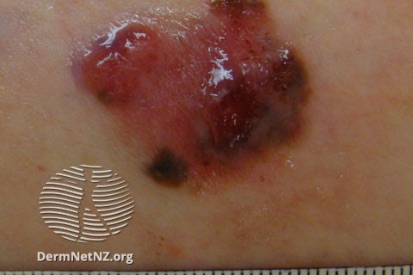
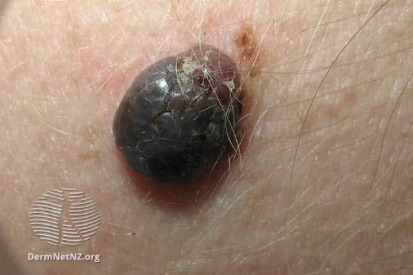
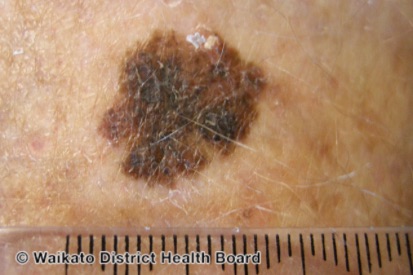
Symptoms of Melanoma
- Melanoma most often presents itself with the change of an existing mole, including change of symmetry, color, or shape.
- Irregular mole borders – scalloped, wavy, or notched.
- Diameter - anything new growing in size.
- Moles that itch, ooze or bleed.
- Melanoma can appear on normal skin tissue and does not always start as a mole.
What Causes Melanoma?
- Melanoma is primarily caused by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin.
- Melanoma is often triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning beds.
- Genetic factors and a history of severe sunburns also contribute to the development of melanoma.
How to Prevent Melanoma
Melanoma FAQs
Melanoma primarily results from prolonged exposure to sunlight, which induces damage to melanocyte DNA. This is a critical factor as melanocyte DNA acts as the blueprint for generating the next generation of melanocytes. Repair abilities for sun damage vary widely among individuals and are likely inherited. Individuals with extensive sun exposure and limited repair ability are predisposed to melanoma, whereas those with minimal sun exposure and robust repair mechanisms are less prone to its development.
Individuals with fair skin, light hair, or light eyes are at the highest risk of developing melanoma, especially if they have a history of frequent sun exposure. Occupations that involve extended periods outdoors or considerable leisure time in the sun pose a particular risk. Conversely, dark-skinned individuals are less likely to develop melanoma. Additionally, those with a personal or family history of melanoma have an increased likelihood of developing the condition.
The prognosis of melanoma hinges on various factors unique to each case, with thickness being a paramount variable. Thick melanomas pose greater dangers as they have increased access to vessels that may facilitate spread (metastasis). Knowledge of melanoma thickness not only allows surgeons to educate patients on their prognosis but also guides the formulation of an optimal treatment plan tailored to the unique characteristics of each case.
Melanoma manifests in diverse appearances, underscoring the importance of regular skin examinations. Dermatologists recommend regular self-skin checks, with attention to hard-to-see areas. Changes in moles, such as asymmetry, irregular borders, color variations, and diameter, can indicate potential melanoma. Early detection through regular monitoring is key to identifying smaller and thinner melanomas.
Some melanomas develop from preexisting moles, a common occurrence given that most individuals have at least one mole on their body. Those with many moles (greater than 100) or atypical moles are at an increased risk of developing melanoma. Atypical moles are often larger with irregular shapes and uneven color. Recognizing the early warning signs involves understanding the ABCD’s—Asymmetry, Borders, Color, and Diameter. Changes in these characteristics should prompt prompt evaluation by a dermatologist.
Diagnosis involves a biopsy, where a sample of the suspicious area is removed and examined under a microscope. Dermatologists use the ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variations, Diameter larger than 6mm, Evolution or change) to assess whether a mole may be melanoma. Regular skin examinations and prompt evaluation of changes are crucial in ensuring early detection and effective management.
From Our QualDerm Family of Providers: Skin Cancer Treatments
Melanoma Treatment Options
We will confirm melanoma through a biopsy and pathological examination and then treat appropriately.
Treatment options for melanoma provided by a dermatologist may include surgical procedures to remove the cancerous tissue, such as excision or Mohs surgery. Additionally, your dermatologist may recommend therapies like immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and characteristics of the melanoma. Close monitoring, regular skin checks, and collaboration with other specialists ensure effective treatment and reduce the risk of recurrence.
If you notice unusual growths on your skin as mentioned above, we highly recommend scheduling an appointment with one of our providers. Annual skin checks are essential for early detection.
Early detection and treatment are crucial elements of comprehensive skin cancer care.
Featured Products for Sun Protection
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!
